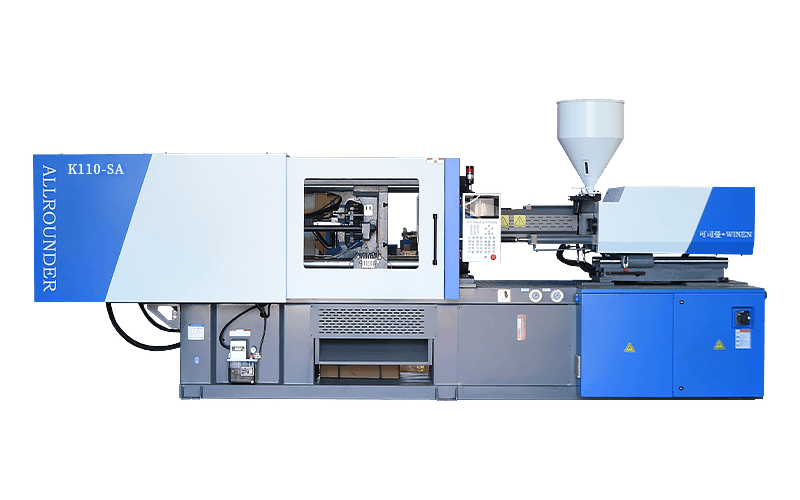
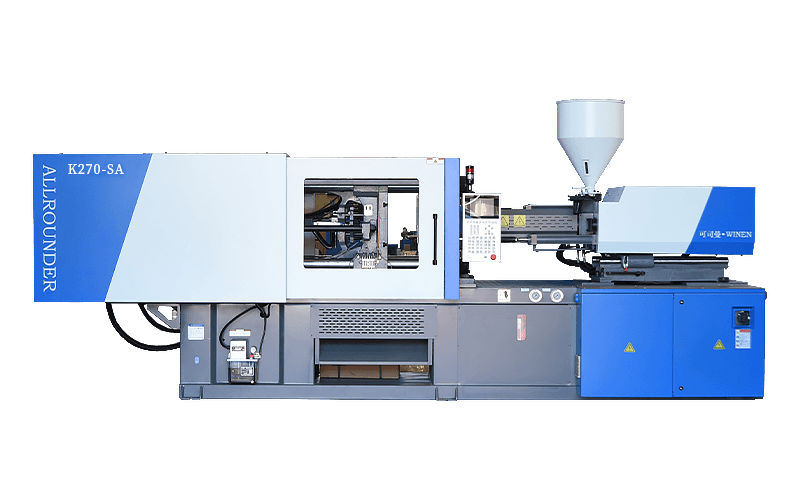
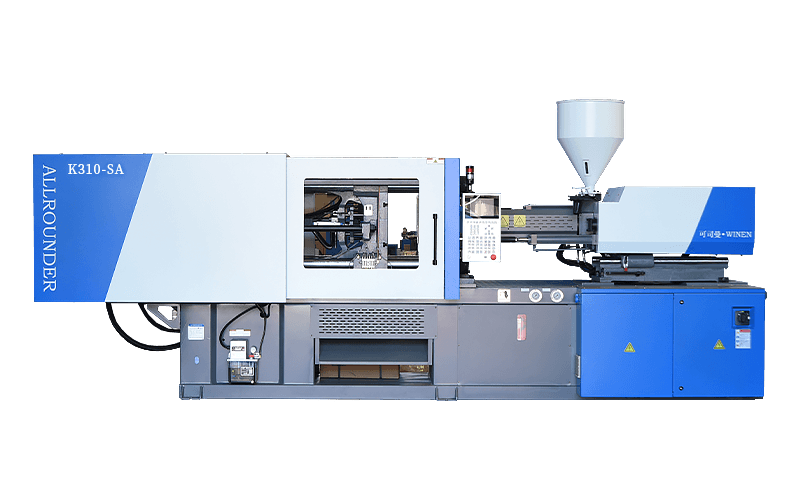
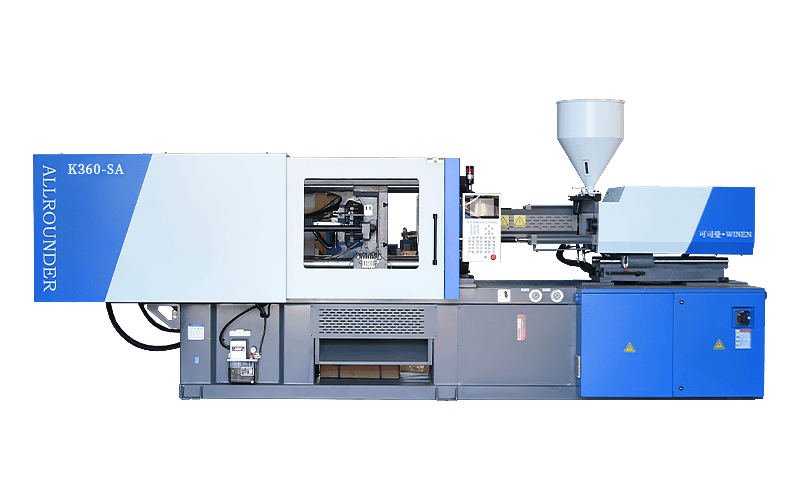
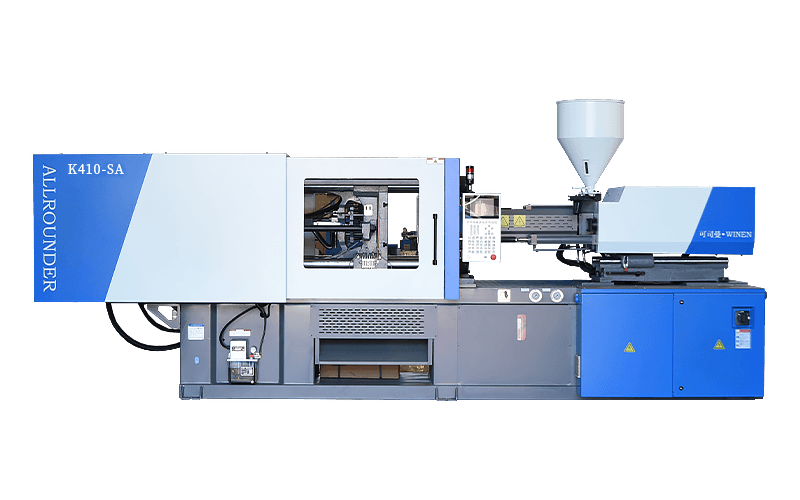
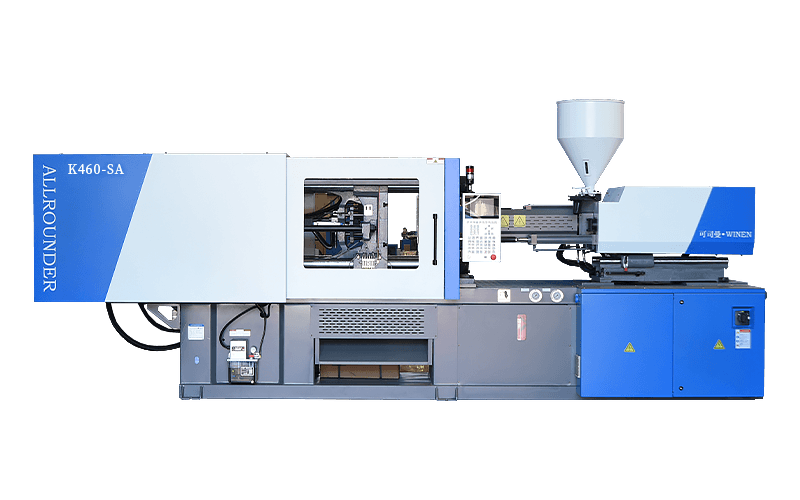
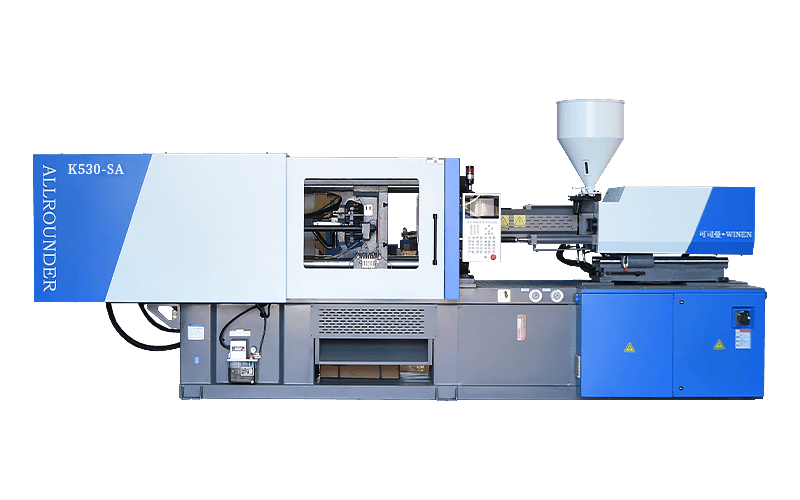
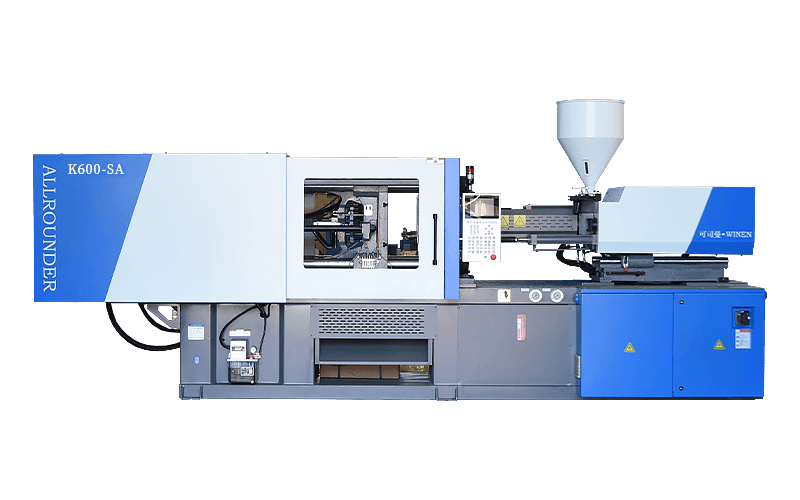
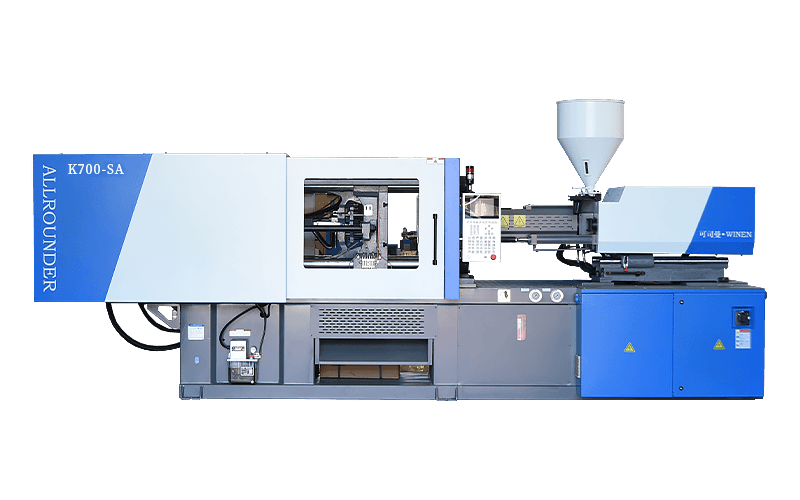
Injection moulding machines are also known as injection moulding machines or injection machines. It is the main moulding equipment for making plastic products of various shapes from thermoplastic or thermosetting plastics using plastic moulds. There are vertical, horizontal and fully electric types. The injection moulding machine heats the plastic and applies high pressure to the molten plastic to make it shoot out and fill the mould cavity.
The working principle of the injection moulding machine is similar to that of the syringe used for injecting. It is the process of injecting the molten plastic (i.e. viscous flow state) into the closed mould cavity with the help of the screw (or plunger) to obtain the product after curing and shaping.
Injection moulding is a cyclical process, each cycle mainly includes: quantitative filling - melt plasticisation - pressure injection - mould filling and cooling - mould opening and removal. The mould is closed again after the part has been removed for the next cycle.
Injection moulding machine operation items: The injection moulding machine operation items include the operation of the control keyboard, the operation of the electrical control system and the operation of the hydraulic system. The injection process action, filling action, injection pressure, injection speed, ejector type selection, barrel temperature monitoring of each section, injection pressure and back pressure adjustment, etc.
The molding process of the general screw injection molding machine is: first of all, the granular or powdered plastic is added to the barrel, and the plastic becomes molten through the rotation of the screw and the heating of the outer wall of the barrel, then the machine is closed and the injection seat is moved forward, so that the nozzle is close to the gate channel of the mould, then the injection cylinder is fed with pressure oil, so that the screw is pushed forward, thus injecting the molten material into the lower temperature with high pressure and fast speed. After a certain period of time and pressure maintenance (also known as pressure-holding), cooling and curing, the product can be removed from the mould (the purpose of pressure-holding is to prevent backflow of molten material in the mould cavity, to replenish the material in the mould cavity, and to ensure that the product has a certain density and dimensional tolerance). The basic requirements of injection moulding are plasticisation, injection and moulding. Plasticisation is a prerequisite for achieving and guaranteeing the quality of the moulded product, while injection must ensure sufficient pressure and speed in order to meet the requirements of moulding. At the same time, due to the high injection pressure, a correspondingly high pressure is generated in the mould cavity (the average pressure in the mould cavity is generally between 20 and 45 MPa) and therefore a sufficiently large clamping force must be available. It follows that the injection unit and the mould closing unit are the key components of the injection moulding machine.
There are three main aspects to the evaluation of plastic products. The first is the quality of appearance, including integrity, colour, lustre, etc.; the second is the accuracy between dimensions and relative positions; and the third is the physical, chemical and electrical properties corresponding to the application. These quality requirements, in turn, vary according to the scale required for the use of the product. Defects in the product are mainly in the design of the mould, the accuracy of manufacture and the degree of wear and tear. However, the fact is that the technicians in the plastics processing plant are often faced with the difficult situation of using technology to compensate for the problems caused by mould defects with little success.
The adjustment of the process during production is a necessary way to improve the quality and yield of the product. As the injection moulding cycle itself is very short, if the process conditions are not well mastered, scrap will continue to flow. When adjusting the process, it is best to change only one condition at a time and observe a few times, if the pressure, temperature and time are adjusted together, it is easy to cause confusion and misunderstanding, and it is not clear what the reason is when problems occur. There are many ways to adjust the process. For example, there are more than ten possible ways to solve the problem of insufficient product injection, and to choose one or two main solutions to the problem in order to really solve the problem. In addition, attention should be paid to the discriminatory relationship in the solution. For example, if the product is sunken, sometimes the material temperature should be increased, sometimes it should be decreased; sometimes the material quantity should be increased, sometimes it should be decreased. It is important to recognise the feasibility of reverse measures to solve the problem.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体